this post was submitted on 31 Oct 2023
285 points (95.2% liked)
Linux
62704 readers
581 users here now
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution (or distro for short).
Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name GNU/Linux to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
Rules
- Posts must be relevant to operating systems running the Linux kernel. GNU/Linux or otherwise.
- No misinformation
- No NSFW content
- No hate speech, bigotry, etc
Related Communities
Community icon by Alpár-Etele Méder, licensed under CC BY 3.0
founded 6 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
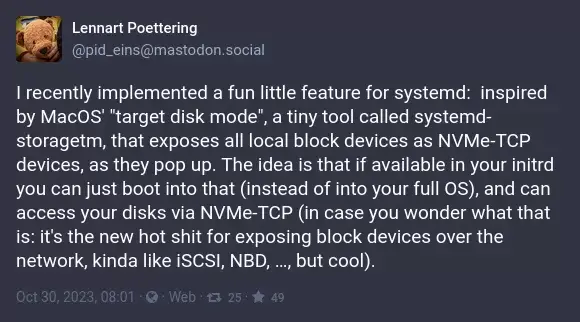
Can someone eli5 pls?
"target disk mode", which this claims to be taking a lot of inspiration from, pretty much turns your computer into an external harddrive - so you can connect another machine to it for direct access. This appears to be trying to accomplish the same, but over the network.
If you've ever stuffed up a machine so badly that the best idea you could come up with, was to take the harddrive out and work on it from another machine - this pretty much allows you to do that. But instead of taking the drive out and putting it an external drive enclosure, you just ask the stuffed up machine to act as the external drive enclosure.
Great answer
Oh okay. Thanks for the simple explanation :)
same, i have no idea what any of that means and i use runit
runit gang !
From what I understand it's basically like a "thin client" type of thing where the client loads the Kernel from local storage up to a certain point and then boots into a rootfs that is somewhere else on a remote server.
Kinda like pxe boot?
Similar but in this case the Linux Kernel/Init System act as the PXE firmware so you don't need a TFTP Server to load initramfs and a Kernel image. And you don't need a NFS or Samba server because the Server has the drive with the rootfs already exposed to the network.
Basically, your system, if asked to, will boot into a limited mode where it exposes its drives over NVMe-TCP. It's like taking the hard drive out and putting it into a different PC, but over the network.