this post was submitted on 11 Sep 2024
67 points (100.0% liked)
Map Enthusiasts
5129 readers
1 users here now
For the map enthused!
Rules:
-
post relevant content: interesting, informative, and/or pretty maps
-
be nice
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
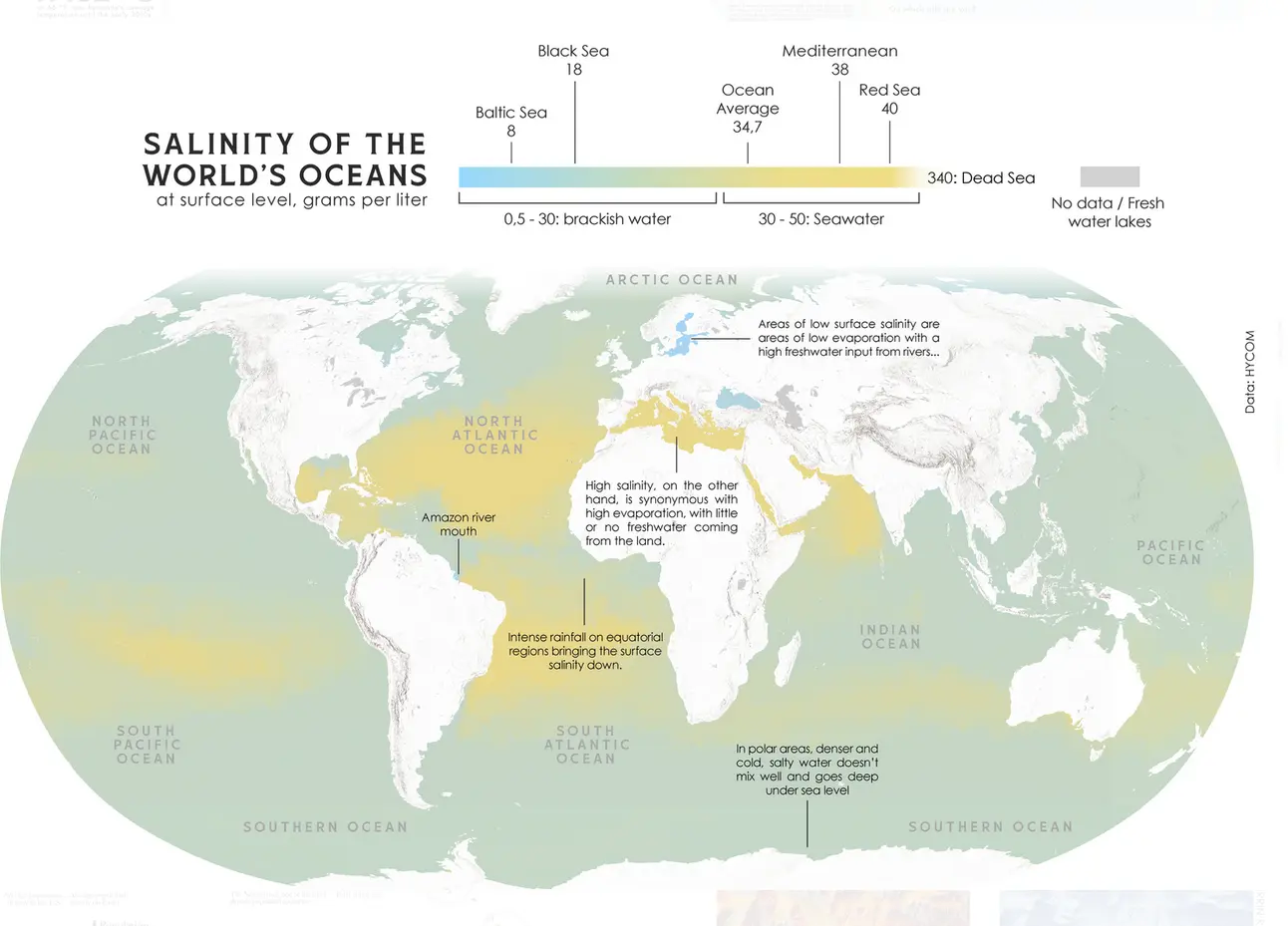
Is thw equatorial concentration from planet spinning and higher density of salt water? Thats cool af
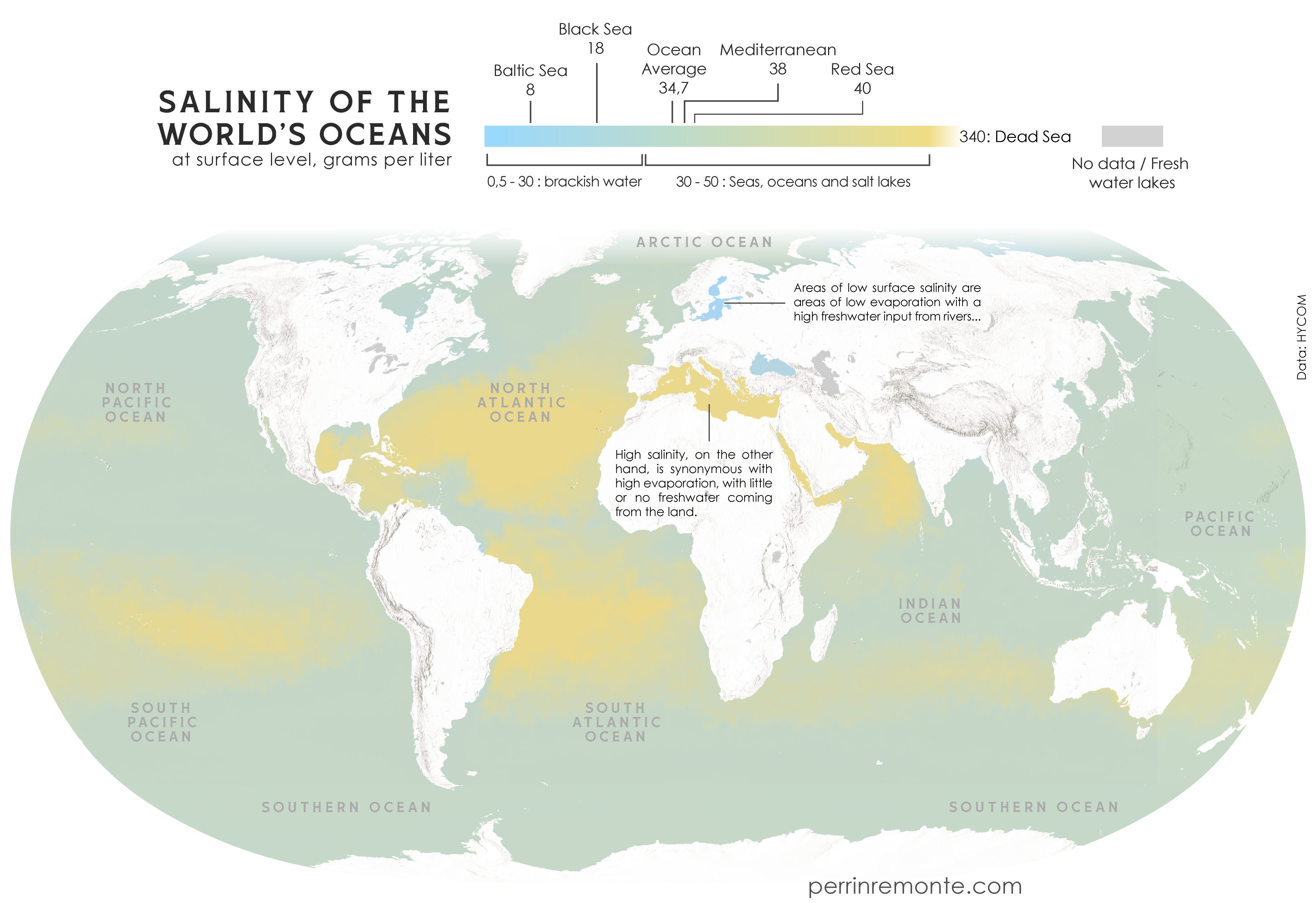
OP has actually posted an update that (indirectly) explains it! https://sopuli.xyz/pictrs/image/f2a9b56e-f915-4932-a35a-d4c3a6e472c9.webp
The equator is actually the less-salty bit in between the two high-salt bands. You'll see the note that says that the less saline areas around the equator are the tropical latitudes that get a lot of rainfall. Because the equator is the most consistently-warm latitude, a lot of water evaporates there and is carried upwards, then falls back down as rain. That air can't keep going up forever though, so it spills out to the north and south. By this point the water has fallen out of it and it has cooled, so it sinks back down and creates dry areas either side of the equator. We can see this as the two yellow bands on the map, and you'll notice that the land in line with those is where we see deserts like the Sahara, the Kalahari, Arabian desert, and central Australia. And also lots of salt at the surface of the ocean, apparently, because there's no rain falling on it.
Makes sense cool that we know this as well.